It’s every sailor’s nightmare: holed and taking on water. For Chris Beeson, the unsinkable Etap turned this sinking feeling into an unusual spa session
Trying to sink an unsinkable boat
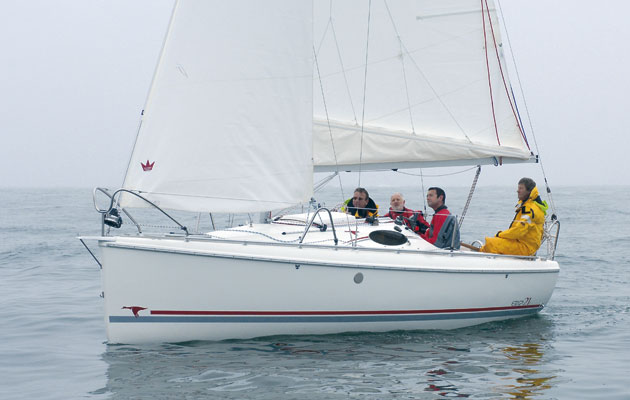
I thought it would feel stranger than it did, wading knee-deep through a flooded boat. While we were being towed out to the Needles, where we’d planned to founder, I was half expecting some mental switch to trip as the water started gushing in, overwhelming me with primal panic. Corporal Jones from Dad’s Navy, I thought. In the event, it was no more alarming than wallowing in a strangely shaped bath with several other men. Scary enough, but some way short of a crisis.
The drama was limited first by the fact that we weren’t allowed to whack gaping holes below the waterline. The new owners of this boat, Grahame and Janine Mason, were understandably reticent about that. They did, however, kindly allow us to open the seacocks in an attempt to send their pride and joy to the bottom. And they did, sensibly, specify that we did so before they took delivery. The UK West Country broker of this yacht, Yachts of Dartmouth, set the wheels in motion.
We were towed out to the Needles by the SeaStart RIB. SeaStart was there to act as a photo-boat but aboard the Etap, I felt a good deal more comfortable knowing that there was something powerful, inflatable and fast nearby should anything go wrong. Once in position – and with nobody having said: ‘Actually, this is a daft idea. Let’s go back, eh?’ – we opened the seacocks.
I was expecting something akin to ‘Old Faithful’ to erupt from the valve, bringing chaos with it. I had imagined the engine room scene from Noel Coward and David Lean’s wartime classic In Which We Serve. The reality was, frankly, disappointing, more like someone spilling a glass of water. This was the second drama limitation. When boats are holed and sinking, the hole is much larger, usually hidden behind joinery, and the ingress much faster.
Having established that we needed to slow to a stop to get any decent ingress, the flooding began. The boat took a while to fill up, even with both the sink and the larger heads seacocks open. It was a good 15-20 minutes before the flare canister started bobbing around. Within half an hour the lids of the bunk lockers began to open and shut with water pressure as the boat rolled in a gentle swell. After 45 minutes, the seacocks were no longer letting water in. We were as low as we could go.
We had a quick bash at sailing but the lack of wind prevented us finding out how her performance was affected by the extra load. Gert, the Etap representative onboard, has done this a few times, most notably in a 24ft Etap, crossing the Channel twice in a day with the boat flooded. He estimated that flooding slows the boat down by 1 knot, not bad considering he reefs to reduce strain on the rig.

Even flooded to the waterline, there was still plenty of freeboard thanks to the closed-cell foam that fills many of her cavities
Once we had all the photos we needed and the novelty of sinking had worn off, the seacocks were closed and the bailing began. We used a 14-litre bucket, scooping on average 8-10 litres each time. The last 30 buckets, filled using a bailer, were brim-full. We emptied 260 buckets in 40 minutes then mopped up the remainder with a sponge. A quick, approximate calculation suggests there were over 2,000 litres of water inside.
Other than the fact that Etap does indeed make unsinkable boats, I’m not sure what we learned. I was hoping to vaccinate myself to the shock of a boat flooding so that, should the nightmare ever strike, I’ll be clearer headed. As it turned out, the height of the drama was a slightly damp mobile phone.
Tech Specs -Etap 21i (Hull no. 549)
LOA: 6.56m (21ft 6in)
LWL: 6.10m (20ft)
Beam: 2.49m (8ft 2in)
Draught: tandem keel: 0.7m (2ft 4in); fin keel: 1.3m (4ft 3in)
Displacement: tandem keel: 1,230kg (2,712lb); fin keel: 1,180kg (2,601lb)
Ballast: tandem keel: 350kg (771lb); fin keel: 300kg (661lb)
Sail area: 23.9m2 (258sq ft)
RCD Category: B/C
Price: £30,000 (new, in 2007)
Website: www.etapyachting.com
BUILDING THE UNSINKABLE
Etap is the only builder of unsinkable yachts and is currently (2007) seeking a Lloyds certificate to that effect. Sadler Yachts used to have a claim to this title before it ceased production but, according to the only standard of unsinkability (that of the French Merchant Marine), unsinkability means that freeboard is reduced by less than 3% of LOA when flooded. Sadlers, though they wouldn’t actually sink, would flood close to deck level.
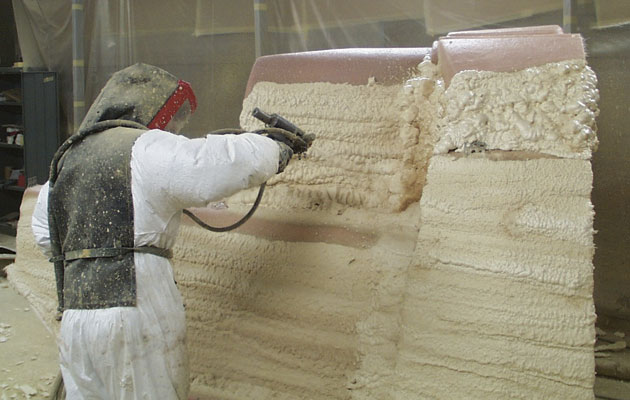
The secret lies in the construction. The whole Etap range, from 21-46ft, uses double-skinned hulls and decks. The spaces between the two skins, and several other pockets throughout the hull and deck, are packed with closed-cell polyurethane foam.
Even if the hull is breached, only the foam damaged by the impact will absorb water. The rest of it, even when exposed to water rather than protected by GRP, has a maximum moisture absorption of 2% after 24 hours.
The result is an unsinkable boat, but there are other benefits. The boat is much stiffer as a result. Also, the foam acts as excellent insulation. It’s warmer below in winter and cooler below in summer. You can leave bedding on an Etap all winter and it will be condensation-free when you return in spring.
Of course, the extra design, materials and labour that go into building an Etap make this a fairly expensive 21-footer but, it you want to, you can buy peace of mind.
DISASTER-PROOFING
Watertight bulkheads
All new ocean racing yachts are fitted with watertight bulkheads. These are sealed, internal bulkheads with a lockable, watertight hatch and as few cable ducts as possible placed as high as possible. To be effective, at least two are required, dividing the boat into roughly equal volumes so that, should one area flood, there is sufficient volume left unflooded to maintain buoyancy. It’s rare for cruising owners to request watertight bulkheads but the more expensive boatbuilders can fit them during build.
Flotation bags
This is a well-established, relatively inexpensive and very effective method of creating buoyancy. These durable bags are easy to store when deflated and can be inflated with carbon dioxide from a SCUBA tank and secured either to anchor points inside the hull or to slings beneath the hull using webbing strops attached to the bags. As GRP supports 25% of its own weight in seawater, you need enough bags to support at least 75% of the boat’s displacement.
PUMPING POWER
A good engine-driven bilge pump will shift about 40 gallons per minute under ideal conditions. The average hand-operated one will only pump half that quantity.
Bilge pump ratings in the manufacturers’ claims are usually for 60 pumps per minute against no resistance, and with no need to lift the water (to a particular height above sea level) before discharging it. A head of 7ft will halve the output.
Any length of piping will rapidly reduce the efficiency of the pump, as length of pipe plays an important role in generating the resistance against which the pump is working.
Just to depress you further, you cannot pump faster than the time it takes the pump to fill and empty. Otherwise the pump loses efficiency. The classic ‘frightened man with a two-gallon bucket’ will shift about 20 gallons a minute. That involves lifting and throwing 20lbs of water every six seconds.
GOING DOWN: FACTS AND FIGURES
The flow of water through a hole is directly proportional to the fourth power of the radius of the hole. A two-inch hole will let in four times as much water as a one-inch hole.
If the hole letting in the water is bigger than the smallest part of the bilge pump pipework, you will surely sink unless you can make the hole smaller.
At a depth of three feet, a hole just one inch in diameter is estimated to pass 34 gallons a minute. Over an hour, that amounts to 2,040 gallons.